Top Linux Commands in 2025
- KevinsinghJ
- Jul 26
- 2 min read
In the ever-evolving world of Linux, mastering the command line remains one of the most powerful ways to boost productivity, streamline system management, and take full control of your operating environment. Whether you're a seasoned system administrator, a homelab enthusiast, or a curious learner diving into Linux for the first time, knowing the right commands can dramatically improve your workflow.
This guide covers some essential Linux commands every user should be familiar with in 2025. From monitoring system resources to managing files, networking, and automating tasks, these commands offer practical tools for everyday use — and a deeper understanding of how Linux works under the hood.
ncdu
I can delete folders through this command and even drill down further into the folders

duf
It shows you the drive usage in a table

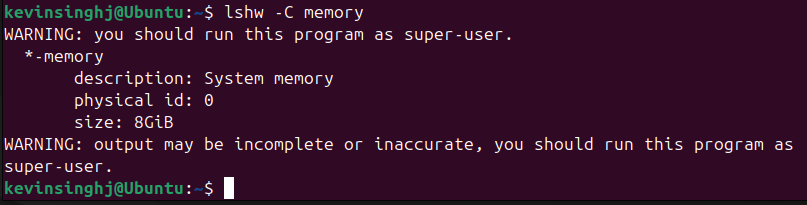
lshw
It’ll show all the hardware resources in my computer

But if i want to specifically just find out about cpu or memory, i can run command lshw -C cpu

Or i can run the command lshw -C memory if i’d like to find out about the memory
mtr
This tracks latency and packet loss hop by hop live

ranger

It’s like a file manager but in the terminal.
glances

It shows you an all-in-one dashboard. It shows you pretty much everything from a glance.
iotop

It’ll show you the stressors of your disk. It’ll show the processes using the most disc IO and it’ll get updated in real time.
stat
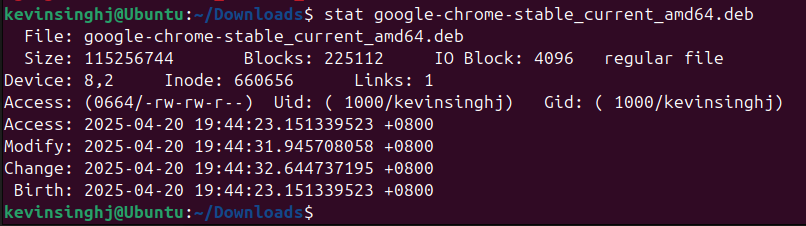
This command will allow you to see every single detail about a file, such as from the day it was born, Inode number
dstat

This command is a real-time system resource monitor for Linux, combining and extending the functionality of tools like vmstat, iostat, netstat, and top.
progress
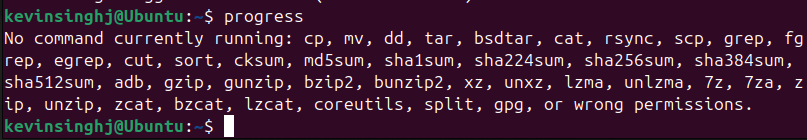
There’s nothing currently running on my system, otherwise it’ll show the progress of the activity
dog

It’s a dns lookup tool, similar to dig command, but it can do more by querying specific record types, show a full dns trace and much more.
lsof -i

I ran the command by specifying the port 443 and it’ll show the process that owns the port
ipcalc

It’s a quick subnet calculator that’ll spit out ranges, mask, wildcard info. For example let’s run the command for an ip and see the result

systemd-analyze blame

If you want to find out why your system is slow and what’s causing it, command systemd-analyze blame will help you to find it out
systemd-analyze critical-chain

We can also run command systemd-analyze critical-chain, highlighting the critical path of dependencies helping us to understand the bottlenecks caused by sequential initialization.
shred

The command rm doesn’t really remove a file completely. It just unlinks it from the file system. If we really want a file to be gone, command shred will help us in getting it done
moreutils
ts

As shown above, by adding ts at the back, we’d be able to see the timestamp of the returned packets
errno

Command errno will help us in finding out the meaning of error number
vidir

Command vidir will help us in changing the directory names and text editors.


